A tattoo is a permanent mark or design made on your skin with pigments inserted through pricks into the skin’s top layer. Typically, the tattoo artist uses a hand-held machine that acts much like a sewing machine, with one or more needles piercing the skin repeatedly. With every puncture, the needles insert tiny ink droplets.
The process which is done without anesthetics causes a small amount of bleeding and slight to potentially significant pain.
The process which is done without anesthetics causes a small amount of bleeding and slight to potentially significant pain.
Tattoos breach the skin, which means that skin infections and other complications are possible, including:
1. Allergic reactions. Tattoo dyes especially red, green, yellow and blue dyes can cause allergic skin reactions, such as an itchy rash at the tattoo site. This can occur even years after you get the tattoo.
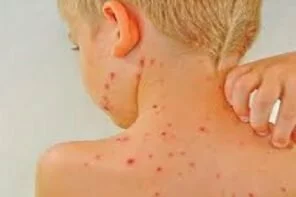
2. Skin infections: A skin infection is possible after tattooing.
3. Other skin problems: Sometimes bumps called granulomas form around tattoo ink. Tattooing also can lead to keloids raised areas caused by an overgrowth of scar tissue.
4. Bloodborne diseases: If the equipment used to create your tattoo is contaminated with infected blood, you can contract various blood borne diseases including tetanus, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
5. MRI complications: Rarely, tattoos or permanent makeup might cause swelling or burning in the affected areas during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exams. In some cases, tattoo pigments can interfere with the quality of the image.
Medication or other treatment might be needed if you experience an allergic reaction to the tattoo ink or you develop an infection or other skin problem near a tattoo.
Medication or other treatment might be needed if you experience an allergic reaction to the tattoo ink or you develop an infection or other skin problem near a tattoo.
By Loveth Ezeugwu
Also Read Healthy diet with proper exercise could reduce asthma symptoms