The breast is made up fat, ducts, lobules, blood vessels and lymph vessels. The lobules produce the milk which is then carried by small tubes (ducts) into about 12 to15 bigger tubes (ducts) which open into the surface through the nipple.
Both breasts in women are usually unequal and even the sizes vary with the period of the monthly cycle; they are a bit bigger and slightly painful about a week to the menstrual period.
The breast has its share of blood vessels and lymph vessels, while every one hears about blood vessels, only a few really hear about lymph vessels but they are very important. They form part of the system in the body that fights against all forms of diseases including cancer. The lymph vessels carry lymph which a clear fluid from the breast tissue to lymph nodes in the armpit and these nodes could become swollen when there is infection or cancer involving the breast.
1. Q. What is breast cancer?
A. As said above, the breast is made up of fat, lobules and ducts among others. Most of the breast cancers result from abnormal growth of cells of the lobules and ducts. In a few cases the abnormal growth may be from the fat and connective tissue.
The cells in our breasts like in other parts of the body are always replacing themselves, new cells being produced as the old ones die off; this is done in a balanced way by genes within the cells.
However this balancing mechanism can fail resulting in more cells being produced than required resulting in a swelling or tumor. If the cells are normal and do not destroy other organs around them, then the tumor is not harmful and not cancerous. However if the cells are abnormal and invade nearby organs, then the tumor is cancerous.
2. Q. How common is breast cancer?
A. Breast cancer is the commonest cancer in women, with over one million women developing breast cancer world-wide every year.
While it also affects men, the number is quite small compared to women. In the developed world where records are better kept, it is one in nine women is likely to develop cancer in her life time.
3. Q. How likely am I to get breast cancer?
A. There are several risk factors associated with breast cancer, a risk factor is something that increases one’s chance of developing a disease. The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age and off course with sex (female). Other risk factors include previous treatment for cancer in one breast, family history of breast cancer, lack of breast feeding, age of first delivery, race (less common in black women) and consumption of hormones for a long time.
4. Q. How can I prevent breast cancer?
A. Breast cancer can be prevented in the following ways:
a. Healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables with minimal fat intake
b. Regular exercise
c. Moderate alcohol intake
d. No smoking
e. Maintaining appropriate weight
f. Oestrogen binding drugs
g. Removal of the breasts
5. Q. When do I get screened for breast cancer?
A. Women aged above 40 years are advised to do screening by mammogram every three years, but it is okay at 50 years and above. The exposure to x-ray is quite harmless and it helps to pick up breast cancer very early.
6. Q. What are the benefits of screening?
A. The benefits of screening include early detection and treatment. Several lives are saved yearly through screening.
7. Q. Is there any relationship between breast feeding and breast cancer?
A. There is a slight advantage in breast feeding a baby, more in women who breast fed at early age and for a long time. They are less likely to develop breast cancer.
Category Archives : HEALTH
Health Effects of Smoking
Smoking has very serious health hazards, yet it is a habit that has refused to leave mankind. The health effects of cigarette smoke is due to its six major constituents:- nicotine, carbon monoxide, arsenic, lead, ammonia, hydrogen cyanide and tar.
Smoking remains the most important preventable cause of illness and death, the estimated number of deaths per annum from smoking is over 4.5 million with more of this occurring in the developed world, more men die from smoking than women.
Smokers die about 10 years earlier than never-smokers, they have twice the risk of heart disease, 10 times the risk of lung cancer, several times the risk of cancer of the mouth, throat, oesophagus, pancreas, cervix, kidney and bladder.
The following health problems also occur more in smokers:-stroke, peptic ulcers, fractures and cataract.
Nicotine, one of the major constituents of cigarette smoke is highly addictive and produces withdrawal symptoms if discontinued. This is what makes it difficult for smokers to quit.
1. Smoking increases risk of cancers.
Smoking is associated with several cancers such cancer of the lungs, mouth, throat, oesophagus, breast, colon, and prostate. Two substances are said to responsible for this:-tar and change in gene (mutation ).
It is the same tar that discolours the teeth; the material that gives the dark colour to smoke.
2. Smoking increases risk of high blood pressure
Nicotine contained in cigarette smoke is said to make the lining of blood vessels more sticky and hence encourages formation of plaque and hardening of the walls of the blood vessels and also narrowing of their inside. When the blood vessels are narrowed it becomes more difficult for the heart to pump blood through them. This leads to increase in blood pressure.
Nicotine also makes the heart beat faster
3. It quickens narrowing of blood vessels.
Cigarette smoke narrows and hardens blood vessels, this reduces blood supply including oxygen to various parts of the body including the heart.
When blood supply to the heart is reduced, the part of the heart muscle affected dies. If the feet or hands are affected, it could result in amputation.
4. It increases risk of prematurity, abortions, low birth weight.
Children of smokers are more likely to be, born premature, of low birth weight and mentally retarded. They also have more frequent chest infections and ear infections than those of non-smokers. Children of Smokers are also more likely to be smokers.
Finally female smokers are more prone to abortions.
5. Smoking worsens complications of diabetes.
It is more difficult to treat diabetes in smokers and the complications of diabetes especially that of narrowing and thickening of blood vessels is made worse by smoking.
6. It reduces the oxygen level in the blood.
One of the constituents of smoke, carbon monoxide, decreases the capacity of the blood to carry oxygen to different parts of the body including the brain. This could lead to the death of the part affected, in case of the feet and hand, amputation could follow.
7. Smoking shortens life by about 10 years.
Owing to the various health problems associated with smoking, smokers die earlier than non-smokers by about 10 years.
SLEEP (3); Causes and Effects of Poor or Inadequate Sleep.
Your internal clock can be disrupted by factors such as nightshift work, traveling across time zones, or irregular sleeping patterns—leaving you feeling groggy, disoriented, and sleepy at inconvenient times. The production of melatonin can also be thrown off when you’re deprived of sunlight during the day or exposed to too much artificial light at night—especially the light from electronic devices, including TVs, computers, tables, and mobile phones.
Even if you’ve enjoyed a full night’s sleep, getting out of bed can be difficult if your alarm goes off when you’re in the middle of deep sleep (Stage N3). If you want to make mornings less painful—or if you know you only have a limited time for sleep—try setting a wake-up time that’s a multiple of 90 minutes, the length of the average sleep cycle. For example, if you go to bed at10 p.m., set your alarm for 5:30 (a total of 7 ½ hours of sleep) instead of 6:00 or 6:30. You may feel more refreshed at 5:30than with another 30 to 60 minutes of sleep because you’re getting up at the end of a sleep cycle when your body and brain are already close to wakefulness.
It’s not just the number of hours in bed that’s important—it’s the quality of those hours of sleep. Each stage of sleep in the sleep cycle offers benefits to the sleeper. However, deep sleep (Stage N3) and REM sleep are particularly important. A normal adult spends approximately 50% of total sleep time in Stage 2 sleep, 20% in REM sleep, and 30% in the remaining stages, including deep sleep.
The most damaging effects of sleep deprivation are from inadequate deep sleep. Deep sleep is a time when the body repairs itself and builds up energy for the day ahead. It plays a major role in maintaining your health, stimulating growth and development, repairing muscles and tissues, and boosting your immune system. In order to wake up energized and refreshed, getting quality deep sleep is essential.
1. Being woken up during the night
Sleep interruption is one of the major causes of sleep deprivation; some individuals are unable to resume sleep while others do so after a long time. The total sleep period for the night is therefore drastically reduced
2. Working night shifts or swing shifts.
A lot of people are on permanent night shift or alternate night and day; the brain on the other hand is programmed for sleep at night not during the day. Consequently those who do night shifts are sleep deprived.
3. Smoking or drinking in the evening
Substances like alcohol and nicotine can disrupt deep sleep. It’s best to limit them before bed time. This also applies to some sedatives and sleeping medicine
4. Fatigue and lack of motivation.
Poor sleep or lack of sleep is a known cause of fatigue; this could be in three forms: generalised weakness, when the person is not able to initiate physical activities; easy fatigability , when the person is unable to complete activities and mental fatigue , when the person finds it difficult to concentrate and has memory loss.
5. Reduced immunity;
Sleep deprivation is associated with reduced ability to fight diseases, consequently those who are sleep deprived suffer from frequent colds and other upper respiratory tract infections. Those who have little sleep frequently have running nostrils.
6. Concentration and memory problems,
Poor sleep or lack of sleep reduces your ability to carry out physical activities with precision; if you are driving, there is increased risk of accident. Concentration is less and decisions are taken less quickly; someone who is sleep-deprived is less creative and finds it difficult to solve problems, to estimate distance. The person also has memory problems.
7. Weight gain
Some of the effects of poor sleep include fatigue, lethargy and lack of motivation, these effects could make you go for sugary drinks to boost your energy; the excess energy could result in excess fat in the body.
Sleep deprivation is also said to have direct link to overeating and weight gain; it is said to affect two hormones (chemicals) in your body that regulate normal feelings of hunger and fullness.
8. Increased risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Fatigue resulting from sleeplessness can drive the affected to take a lot of sugary energy drinks with the possible development overtime of excess sugar in the blood (diabetes) and its complications of heart disease and disease of the blood vessels. Lack of sleep is also associated with depression and bipolar disorders.
HEALTH TIPS ON STRESS
One of the terms most difficult to define is stress, but let us simplify it by saying that you are under stress when your well-being is challenged or threatened and you are prompted to respond. Stress as a challenge can propel one to achieve greater height but when stress is prolonged and uninterrupted, it can affect the health of the person concerned.
Stress can be due to loss of loved ones, natural disasters (earthquake, floods ), workload, problems in the home, problematic relationships etc, these are all stressors. A stressor is anything that puts you under pressure or threatens your well-being physically or mentally.
Stressors cause the release of hormones which prepare the body to deal with the challenge.
When stress is prolonged and persistent, it impacts negatively on health. Some of the health problems associated with stress are discussed below:
1. Heart Disease.
Four symptoms of stress –anxiety, depression, loneliness and hostility are closely associated with heart disease-a disease which affects the blood vessel supplying blood to the heart. Several studies have established a close relationship between depression and heart disease/ sudden death. The same applies to anxiety, the latter is linked to heart attacks. These sudden deaths from heart attacks are due to activities of nerves and hormones which directly or indirectly affect the heart.
2. High Blood Pressure
Stress accompanied by anxiety is closely linked with high blood pressure . This could be due to activities of hormones and/or nerves which affect the heart and blood vessels. The activities of these hormones and nerves can quicken the heart rate and increase the force of contraction of the heart, a usual response to fright
3. Asthma
Stress does not bring on an asthmatic attack in an asthmatic. However stress is known to bring on increased breathlessness in an asthmatic, that means an asthmatic feels more breathless under stress than a non- asthmatic but it does not have a causal association with asthma
4. Alcoholism
One of the behavioural symptoms of a person under stress is increased alcoholic consumption. This is taken by the stressed person in order to relax but this could lead to dependence on alcohol and gradual increase in the daily volume consumed. If the stress is prolonged and persistent, alcoholism can follow with its attendant health problems.
5. Smoking
Some people under stress take to smoking to cool their nerves. That they have a feeling of relief when they smoke could lead to dependence on cigarette/cigar. Smoking is a very difficult addiction to break and health problems of smoking are many.
6. Sexual Problems
Stress can cause sexual problems in both males and females. The sexual problems include loss of desire (male and female), poor erection and premature discharge (male), lack of arousal (female), failure to achieve orgasm (male and Female). If untreated, poor erection can lead to impotence.
7. Ulcer in the Stomach/Intestine
Stress can cause ulcers in the stomach and intestine (duodenal) or make them worse. This is directly due to the increased production of acids and some other chemicals by the stomach which eat the inside of the stomach and the beginning of the intestines. This problem disappears if the stress is properly managed on time.
Stressful events are associated with onset of diabetes in a lot of people. Diabetic conditions are more difficult to control when the patient is under stress than under normal conditions. In-fact, when under treatment, stressed diabetic patients respond better to treatment if the stress is being adequately managed at the same time. This pattern may not be unconnected with hormones produced by the body when stressed.
HEALTH TIPS ON DENGUE FEVER
Dengue fever is a very old disease, first recognised in China about two thousand years ago. It is common in South -East Asia and the Pacific region but also occurs in North America, Africa, the Caribbean and the Mediterranean region.
1.What is Dengue fever?
Dengue fever is a disease caused by a virus and characterised by high fever, body pains, severe headache, bleeding into the skin and/or nose bleeds.The fever is more important to us today because its symptoms are similar to those of Ebola fever. Both have no cure, only supportive treatment is available. Death from dengue is also high but spread is not as rapid as that of Ebola fever. Occasionally epidemics of the disease occur.
2.What causes dengue fever?
Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus; there are four types of dengue virus.

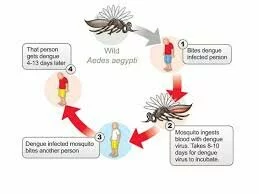
3.How does dengue fever spread?
Dengue fever is spread by female mosquitoes- Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus.The latter is said to be more incriminated in Nigeria; the last case of Dengue reported recently is linked to this mosquito.
The mosquito bites man during daytime, carries the virus if the man is infected and may pass it on to any other person it bites.
Occasionally, a pregnant woman may pass the virus to the baby in her womb.
4.Who can be affected by dengue fever?.
Dengue fever affects infants, children and adults.
Those living in areas where rainfall is high are more at risk because it encourages mosquito breeding and the temperature shortens the development period of the virus to make it dangerous.
Another group at risk are those who live in the same house with someone with dengue fever.
The spread of the disease is also facilitated by the presence of the infected mosquito where large number of people occupy a place at the same time such as cinema houses, hospitals, offices, hospitals, schools,and factories.
A few mosquitoes could bite a lot of people.
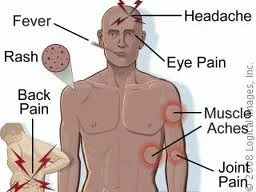
5.Symptoms and signs of dengue fever.
Dengue fever is characterised by high fever, severe headache, body pains, nose bleeds, skin bleeds, and shock.

6.Prevention
The disease can be prevented in two ways;
a. you can deal with the mosquito by preventing it from breeding; any thing that can contain water like spoilt tyres, bottles, dead leaves, open gutters, unused ponds should be discouraged and discarded if possible.
b.you can prevent mosquito bites by wearing long sleeved dresses, and trousers especially if going to places where there will be a lot of people.
HOW THE ELDERLY CAN BE ABUSED
We sparingly hear of elderly abuse, what we hear of all the time is child abuse, more so in Nigeria where the senior citizens do not enjoy any privileges. Defining the elderly is a bit difficult in Nigeria, in some countries it is 65 years and above, but recently the retirement age for certain government employees was moved to 70 years. Besides a lot of people are still quite active above the age of 70 years.
For the purpose of this Health Tip, let us take the elderly to be persons who are 70 years and above.
It is said that those above 64 years in our society make up about 5 percent of the population, that means, in our population of about 170 million, only about 9 million persons are above 64 years.
The elderly are disadvantaged in the society, they are weak physically, not quite healthy, prone to illnesses, do not earn money in most cases. We can therefore easily abuse them without realizing it. I must add that abuses tend to occur more in poor families.
Here is how we can abuse the elderly.
1. Physical Abuse
Elderly people are abused regularly but more in rural areas and especially women. The situation is worse if the woman has no children or the children are not around. Even within the family, the elderly can be physically abused by the direct children and even the grandchildren. There have been instances of old women being accused of witchcraft and beaten to death. Physical abuse is not as common with old men.
We as children must find time to keep in touch with our parents at home, it sends signals to those near them that they are not alone.
2. Sexual Abuse
We often read of sexual abuse of elderly women by much younger men. This is a most heinous act of rape, the elderly is weak and sex could be a very painful experience not to talk of humiliation and the risk of sexually transmitted diseases. Those most at risk are the widows who in most cases live alone.
Again being in regular contact with our parents scares away potential perpetrators. In a few cases such heinous crimes are committed by close family members.
3. Psychological abuse.
This sort of abuse is usually by family members and close neigbours. It could be by use of abusive words, taunting, disrespect, making jest of the person, dismissal of whatever the old person says and lack of consultation before taking decisions concerning the elderly person. We all may have been guilty of this occasionally when we were younger but with hindsight, things could have been done better.
The elderly person whether educated or not is a reservoir of wisdom and we can benefit from their wise counsel.
We must respect the elderly, seek their opinion on issues which concern them, love them genuinely and talk to them regularly if we are not living together..
4. Economic Abuse
The elderly, especially the uneducated, do not work and so do not earn any money, they depend solely on their children and relations. Consequently, most of the time, they are without money. The elderly need to have some money of their own, a monthly allowance will do.
In some developed countries, they get monthly allowance, Sometimes in June this year, Anambra State started a social welfare package for persons aged 70 years and above.
5. Neglect
Many children neglect their parents, some cannot cope with the problems that come with old age, the wrinkled skin, sometimes slow speech, memory loss among others. That is wrong, very wrong.
We must care for, respect and love the elderly.They would surely appreciate that and live much longer.
Myths and Facts On Sleep
Many of us try to sleep as little as possible. There are so many things that seem more interesting or important than getting a few more hours of sleep, but just as exercise and nutrition are essential for optimal health and happiness, so is sleep. The quality of your sleep directly affects the quality of your waking life, including your mental sharpness, productivity, emotional balance, creativity, physical vitality, and even your weight. No other activity delivers so many benefits with so little effort! Even minimal sleep loss takes a toll on your mood, energy, and ability to handle stress.
Sleep isn’t exactly a time when your body and brain shut off. While you rest, your brain stays busy, overseeing a wide variety of biological maintenance that keeps your body running in top condition, preparing you for the day ahead. Without enough hours of restorative sleep, you won’t be able to work, learn, create, and communicate at a level even close to your true potential.
As you start getting the sleep you need, your energy and efficiency will go up. In fact, you’re likely to find that you actually get more done during the day than late at night. By understanding your nightly sleep needs and what you can do to bounce back from chronic sleep loss, you can finally get on a healthy sleep schedule.
1. Getting just one hour less sleep per night won’t affect your daytime functioning.(false)
You may not be noticeably sleepy during the day, but losing even one hour of sleep can affect your ability to think properly and respond quickly. It also compromises your cardiovascular health, energy balance, and ability to fight infections.
2. Your body adjusts quickly to different sleep schedules.
Most people can reset their biological clock, but only by appropriately timed cues—and even then, by one–two hours per day at best. Consequently, it can take more than a week to adjust after traveling across several time zones or switching to the night shift.
3. Extra sleep at night can cure you of problems with excessive daytime fatigue (false).
The quantity of sleep you get is important, sure, but it’s the quality of your sleep that you really have to pay attention to. Some people sleep eight or nine hours a night but don’t feel well rested when they wake up because the quality of their sleep is poor.
4. You can make up for lost sleep during the week by sleeping more on the weekends (false).
Although this sleeping pattern will help relieve part of a sleep debt, it will not completely make up for the lack of sleep. Furthermore, sleeping later on the weekends can affect your sleep-wake cycle so that it is much harder to go to sleep at the right time on Sunday nights and get up early on Monday mornings.
5. Lack of sleep affects your judgment, coordination, and reaction times (true).
While it may seem like losing sleep isn’t such a big deal, sleep deprivation has a wide range of negative effects that go way beyond daytime drowsiness. Lack of sleep affects your judgment, coordination, and reaction times. In fact, sleep deprivation can affect you just as much as being drunk.
The effects include:
• Fatigue, lethargy, and lack of motivation
• Moodiness and irritability
• Reduced creativity and problem-solving skills
• Inability to cope with stress
• Reduced immunity; frequent colds and infections
• Concentration and memory problems
• Weight gain
• Impaired motor skills and increased risk of accidents
• Difficulty making decisions
• Increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other health problems
6. Smoking or drinking in the evening can affect the quality of your sleep.(true)
Substances like alcohol and nicotine can disrupt deep sleep. It’s best to limit them before bed. This also applies to some sedatives and sleeping medicine
7. Sleep deprivation can make you put on weight (true).
Some of the effects of poor sleep include fatigue, lethargy and lack of motivation, these effects could make you for sugary drinks to boost your energy; the excess energy could result in excess fat in the body.
Sleep deprivation is also said to have direct link to overeating and weight gain; there are two hormones in your body that regulate normal feelings of hunger and fullness. Ghrelin stimulates appetite, while leptin sends signals to the brain when you are full. However, when you don’t get the sleep you need, your ghrelin levels go up, stimulating your appetite so you want more food than normal, and your leptin levels go down, meaning you don’t feel satisfied and want to keep eating. So, the more sleep you lose, the more food your body will crave for.
Some Health Problems of Teenage Girls
A teenage girl is one aged between 13 and 19 years. This period witnesses rapid and far reaching changes both physically and psychologically in girls. They begin to develop breasts and also become aware of themselves as women; thus attracting the attention of males.
1.Teenage Pregnancy
One of the greatest problems of teenage females is teenage pregnancy; this is defined as pregnancy before the age of 20 years. This could be due to lack of experience, lack of knowledge, rape and other forms of sexual assault.
2.Maternal Deaths
Studies have shown that girls aged 15-19 years are twice as likely to die from childbirth as are women in their twenties.
Also, girls aged less than 15 years are five (5) times more likely to die from child birth than women in their twenties.
This may be due to the following reasons: teenage girls are not physically and psychologically ready for pregnancy, poor knowledge on ante–natal or lack of knowledge, poverty, neglect by family and society, poor access to healthcare system.
3.Low Contraceptive Usage
Studies have shown that the use of contraceptives among teenage girls is very low yet they could be very sexually active. This is largely due to poor knowledge. Parents are reluctant to discuss sexuality with their teenage daughters, consequently the little knowledge obtained is from peer group.
4.Unsafe abortion
Teenage girls are more exposed to unsafe abortions. Unsafe abortion is the termination of unwanted pregnancy either by unqualified persons or in an environment lacking minimal surgical standards or both.
Pregnant teenage girls are usually at a loss as regards where to go for an abortion; may not have the money because the teenage male usually responsible denies the pregnancy, she is in most cases sent out by the parents and also jobless.
Consequently she looks for the cheapest method of removal either surgically or medically, that is when a quack comes in.
Parents should be supportive in such situations as the teenager could still turn out to be very successful in life.
5.High prevalence of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Teenage girls aged 15-19 years have higher incidence of sexually transmitted diseases than women in their twenties. This is due to poor knowledge of such diseases and the use of condoms.
6.Premature birth
One of the known causes of premature birth is age, pregnancies of females below 19 years of age more likely to end in premature birth than of females in their twenties.
Premature babies have several problems.
HEALTH ADVISORY OF THE DAY:
You can reduce your risk of stroke by 4 actions: A. Daily exercise for 30 minutes, B.Eat fruits/vegetables daily, C. Do not smoke D. Minimise alcohol intake.
HEALTH QUOTE OF THE DAY:
Sometimes I get the feeling that aspirin companies are sponsoring my headaches-----Terri Guillemets (American Anthropologist)



